Diabetes is a condition that causes a person’s blood sugar level to become too high. There are 2 main types of diabetes :
- Type 1 diabetes – a lifelong condition where the body’s immune system attacks and destroys the cells that produce insulin.
- Type 2 diabetes – where the body does not produce enough insulin, or the body’s cells do not react to insulin properly.
The Gibraltar Health Authority is in the early stages of developing a diabetes register in order to understand the prevalence of diabetes amongst the Gibraltarian population. However, this data is still in very preliminary stages and is in the process of being validated. As a result, the data displayed on this page is subject to change.
Gibraltar statistics on Type I Diabetes
Figure 1: Type I Diabetes – Of all individuals identified as having type 1 diabetes on the GHA primary care system between 2016-2023 the following graph shows the percentage of these individuals by age group.
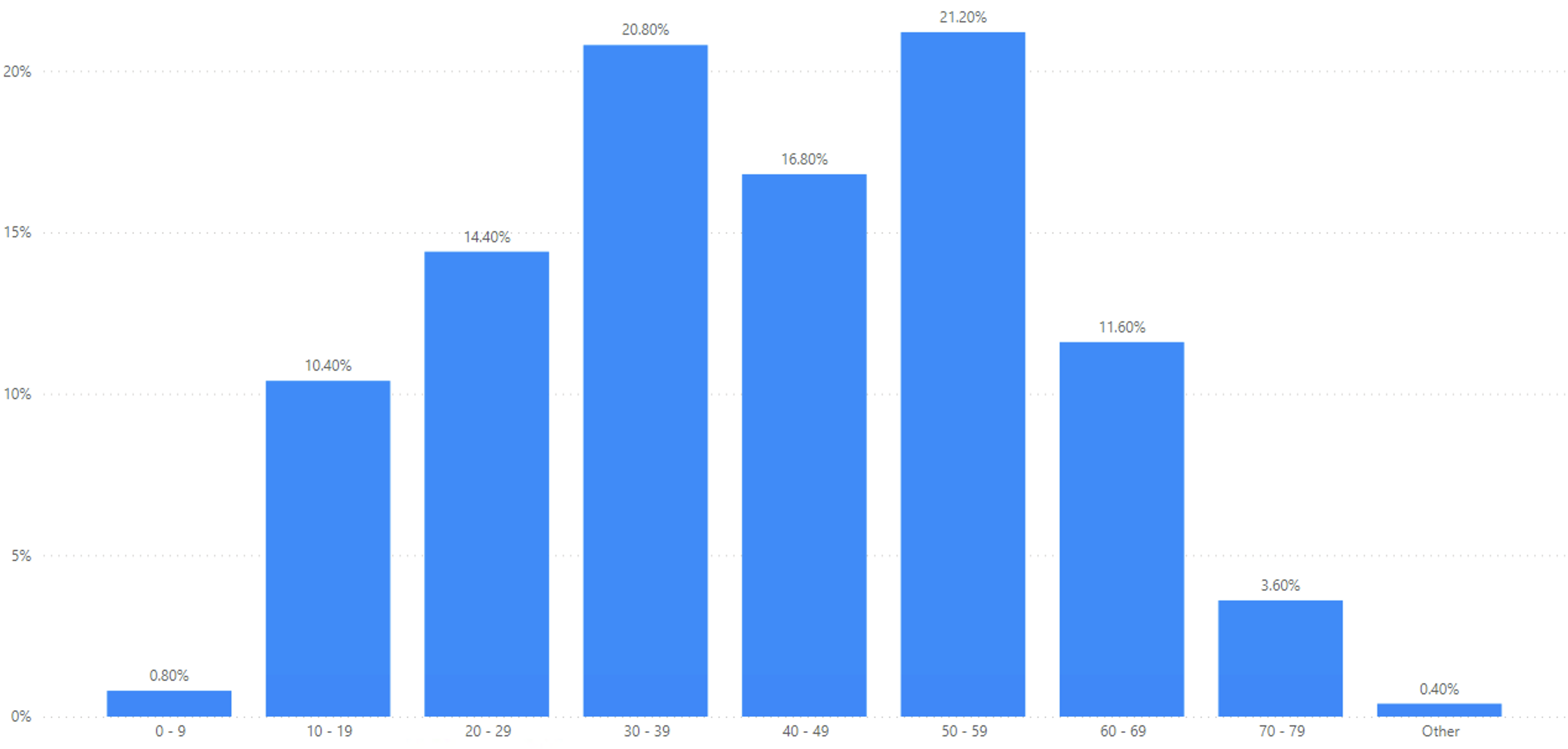
Data Source: Gibraltar Health Authority
Type 1 diabetes can appear at any age, however children and young adults typically have the highest incidence of new on-set type 1 diabetes. Of all patients recorded with Type 1 diabetes at the Gibraltar Health Authority, 10.40% are aged 10-19 years and 14.40% are aged 20-29 years.
Genetics and a family history are risk factors for type 1 diabetes. You are at a slightly higher risk of type 1 diabetes if your mother, father, sibling has it. As from November 2023, 21.20% of people with Type 1 diabetes are aged 50-59 years old. Of those with Type 1 diabetes, the 50-59 year age group have highest incidence, closely followed by 30-39 year group.
Figure 2: Type I Diabetes – Of all individuals identified as having type 1 diabetes on the GHA primary care system between 2016-2023 the following graph shows the percentage of these individuals by sex.
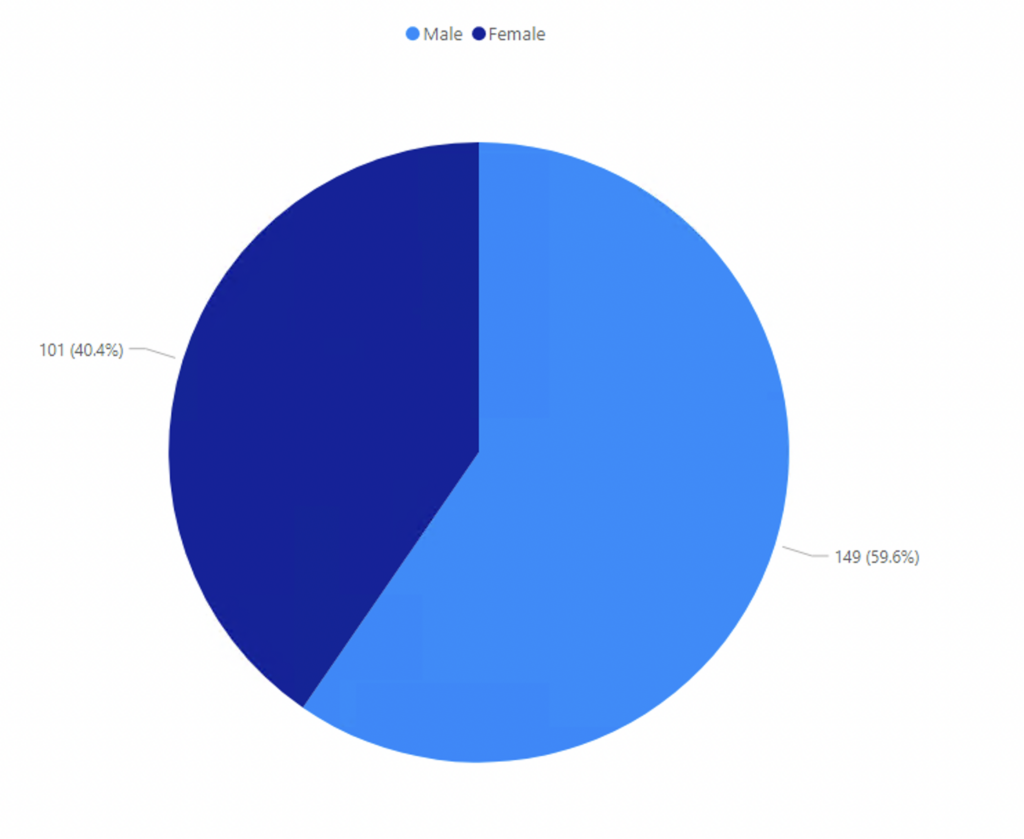
Among the population sample, more males suffer from type 1 diabetes than females, with 59.6% of males living with type 1 diabetes compared to 40.4% of females.
Gibraltar Statistics on Type II Diabetes
Figure 3: Type II Diabetes – Of all individuals identified as having type 2 diabetes on the GHA primary care system between 2016-2023 the following graph shows the percentage of these individuals by age group.
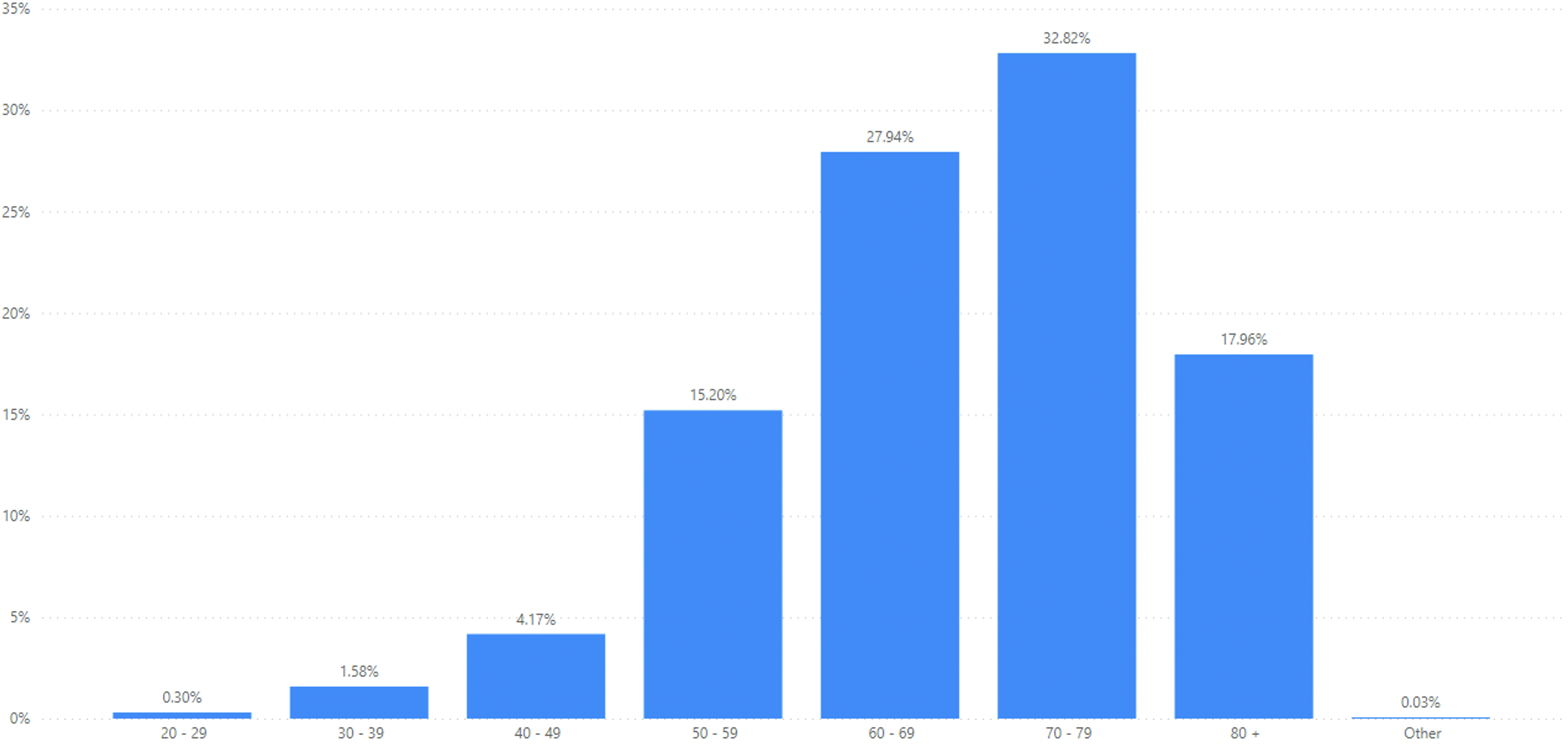
The median age of person in population suffering from type II diabetes is 70 years. The median age at diagnosis is 59 years. Of all patients with a diagnosis of type 2 diabetes, 32.82% are aged in the 70-79 age group.
UK studies found have that the median age of diagnosis for type 2 diabetes between 2009-2018 is 60.4 years in males and 61.7 years in females (Pal et al., 2021).
Figure 4: Type II Diabetes – Of all individuals identified as having type 2 diabetes on the GHA primary care system between 2016-2023 the following graph shows the percentage of these individuals by sex.
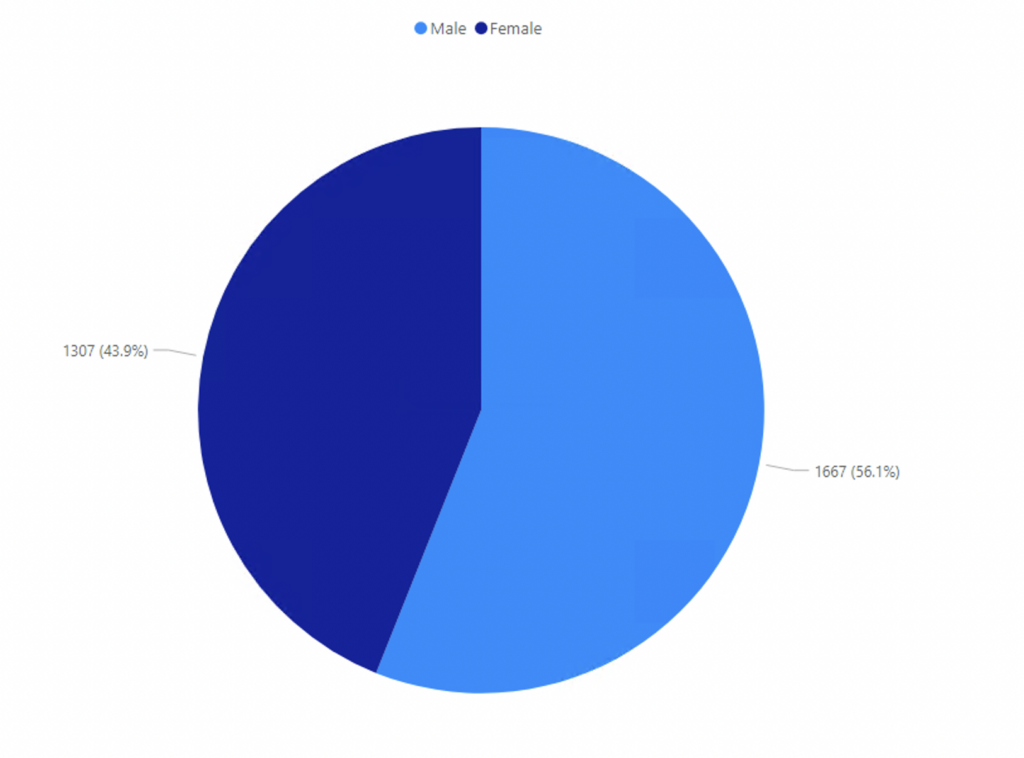
Males in the population sample are more likely to suffer from type II diabetes compared to females, with 56.1% of males living with the condition and 43.9% of females. These findings are inline with global statistics, as it is estimated that worldwide, 17.7 million more men than women suffer from diabetes mellitus.
Risk factors of Type 2 diabetes
Risk factors for type 2 diabetes include:
- Increasing Age
- Hypertension (High blood pressure)
- Smoking
- Sedentary lifestyle
- High waist measurement
- Poor sleep hygiene
- Overweight or obese
- Family member (parent, brother, sister or child with type 2 diabetes)
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
- Ethnicity – People of South Asian descent and African-Caribbean or Black African descent are at increased risk.
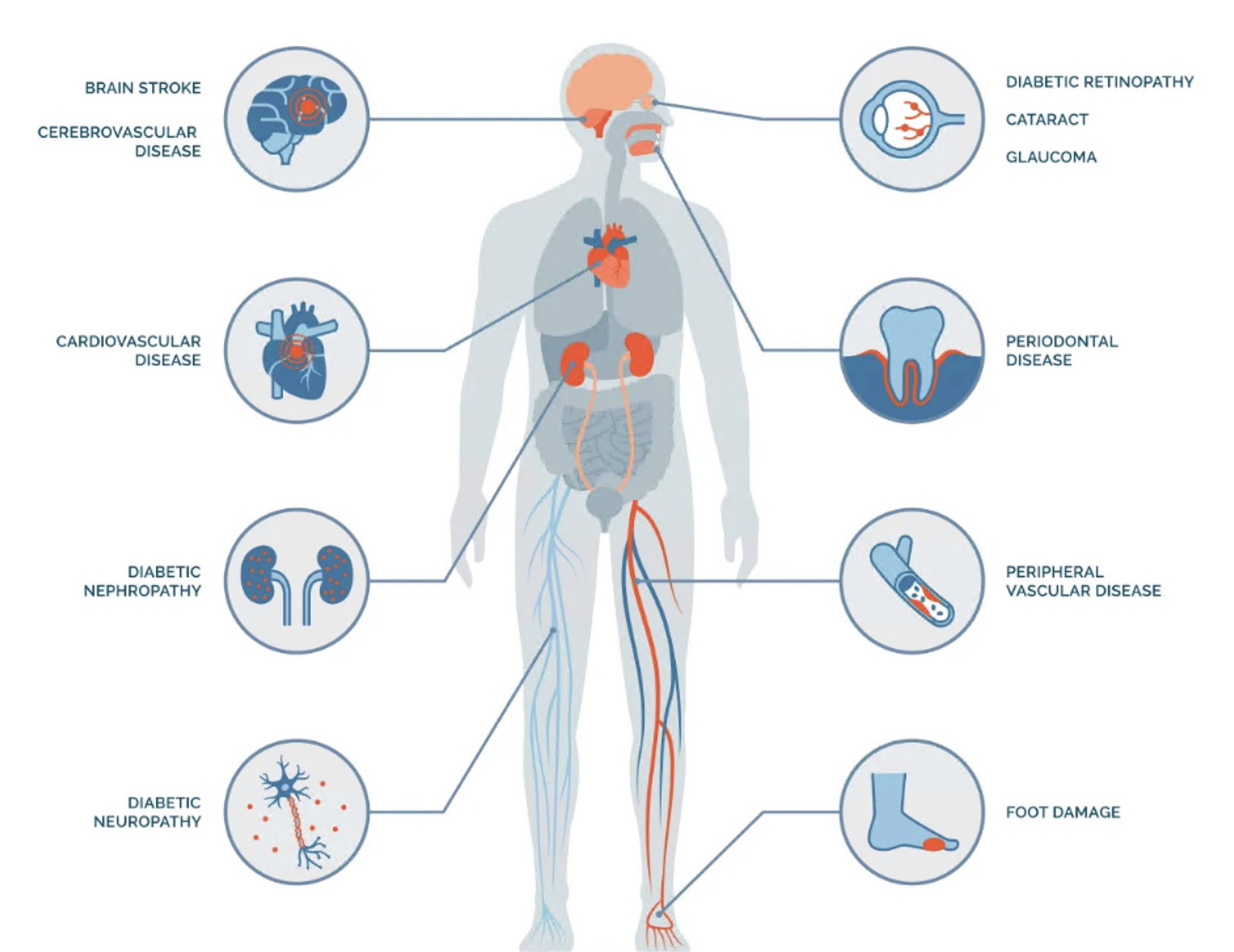
Complications of Type 2 Diabetes
If diabetes is not treated, it can lead to various health complications and affect multiple systems. Untreated Type 2 diabetes can lead to complications including:
- Heart disease and stroke
- Loss of feeling and pain (nerve damage)
- Foot problems – like sores and infections
- Vision loss and blindness
- Miscarriage and stillbirth
- Problems with your kidneys
- Sexual problems (NHS, 2023).
It is important to keep up to date with regular check ups and attend diabetic retinopathy screening appointments in order to avoid complications.
Figure 5: Complications of Type 2 Diabetes. Source: Endocrine Society
Living with diabetes – Useful resources
Page last reviewed : December 2023

